A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle equipped with two or more engines, operating under different principles, but that can alternate propulsion. The most widespread form of hybrid propulsion is associated with a combustible engine, powered by a fuel, and an electric motor, powered by a generator or a battery. The concept of the hybrid engine was first introduced at the turn of the twentieth century. Submarines were the first vehicles to take advantage of dual propulsion, one used to move deep underwater and one used to move near the surface of the water. During that same period, German engineer Ferdinand Porsche built the first hybrid car in history in 1899. The four wheels of the Lohner-Porsche were equipped with many electric motors, powered by a generator, which in turn was reliant on a combustible engine.
The excessive weight of hybrid cars and the increased affordability of automobiles with combustion engines led to diminished interest from the global automotive market for the hybrid car for over half a century. During the second half of the twentieth century, however, the hybrid automobile enjoyed newfound popularity as a result of rising fuel prices due to the oil crisis and the pollution caused by gas burning engines. Free from the mileage limits of the typical electric car and less-polluting then cars equipped only with internal combustion engines, the hybrid car makes the most of the advantages of both solutions. The electric motor may in fact occur in the thermal compensating deficiencies and inefficiencies and consequently saves its owner fuel costs and creates less pollution. The production of hybrid cars is now a steady and progressive growth industry and an integral part of the commercial potential of major international car manufacturers.
The excessive weight of hybrid cars and the increased affordability of automobiles with combustion engines led to diminished interest from the global automotive market for the hybrid car for over half a century. During the second half of the twentieth century, however, the hybrid automobile enjoyed newfound popularity as a result of rising fuel prices due to the oil crisis and the pollution caused by gas burning engines. Free from the mileage limits of the typical electric car and less-polluting then cars equipped only with internal combustion engines, the hybrid car makes the most of the advantages of both solutions. The electric motor may in fact occur in the thermal compensating deficiencies and inefficiencies and consequently saves its owner fuel costs and creates less pollution. The production of hybrid cars is now a steady and progressive growth industry and an integral part of the commercial potential of major international car manufacturers.
RELATED


DOG


ARCHIMEDES' PRINCIPLE


FLY
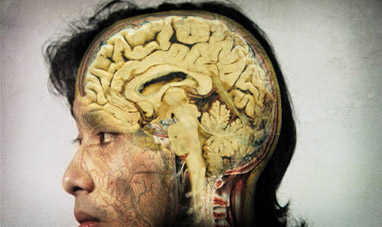

THE BRAIN


GOOGLE


CITRUS FRUIT
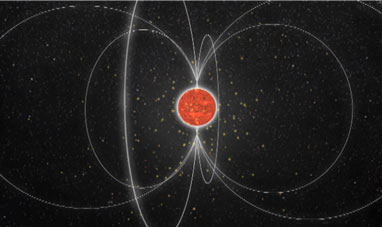

PULSARS


STARFISH


HYDROPOWER


QUASARS


SQUID


BLACK WIDOW SPIDER
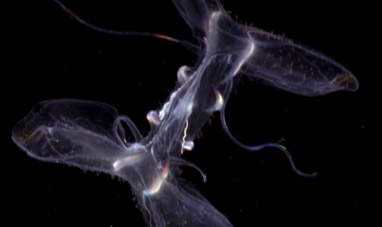

JELLY FISH


IGUANA
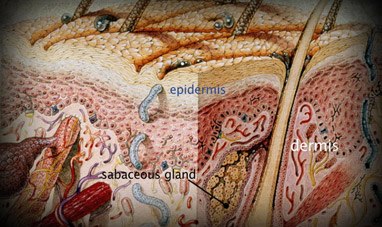

SKIN


TWITTER


SALMON


HERMIT CRAB


AIDS


EAGLE


AXOLOTL


WHEAT
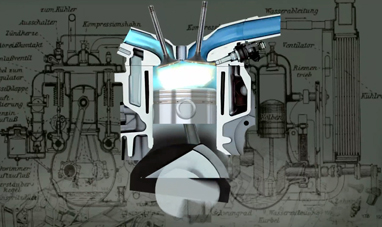

CARS
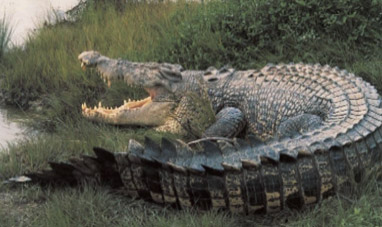

CROCODILE


TORTOISE
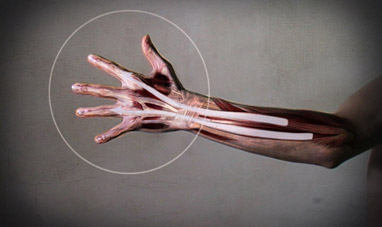

THE HANDS


BLACK HOLES


MOSQUITO


CACTUS


OSTRICH


BEE


FLEA


LADYBUG


ANACONDA


GARLIC


METEORITES