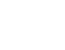The tiger is a carnivorous mammal of the Felidae family.There are currently around 5 subspecies in existence, all of which live in Asia. The best known is the Bengal tiger, [Panthera tigris tigris] which populates India, while the largest is the Siberian tiger, [Panthera tigris altaica] which can stretch over 3 meters in length and weigh more than 300 kilos.White tigers, although famous, are not a subspecies. Their black and white fur and blue eyes are the result of a rare genetic mutation which occurs usually among Bengal tigers. The tiger is a predator and usually eats monkeys, deer and boars. However, it is also capable of preying on large buffalos. It sets out at dusk and hunts through the night, making the most of its fine sense of hearing and eyesight. When a tiger spots its prey, it approaches the animal silently, hiding in the darkness. If it attacks by day, the tiger takes advantage of its striped fur to hide in vegetation. It then launches a lightning-fast attack, biting its prey at the throat and keeping it pinned down with its powerful legs and retractable claws. To survive, a tiger needs to consume roughly 9 kilos of meat per day. The tiger is a solitary animal, and a single specimen may control a territory of up to 100 square kilometers. Males and females only come together during the mating season. Following a gestation period of around 100 days, the female gives birth to 2 or 4 cubs, which she feeds with her milk for around 6 months. After 18 months the cubs are already strong and active, but they stay with their mother until they are three, learning and improving their hunting skills. The tiger is both feared and admired by man. The elegance and power of its sinuous body have made it sacred in many Asian cultures. According to some popular beliefs, tigers keep demons away. The tiger has also inspired one of the Chinese martial arts, giving rise to a style characterized by fast, powerful moves.
RELATED


BOA


SEA URCHIN


HYDROPOWER


CHAMELEON


GECKO


EBAY


ERIS


GROUPER


CATERPILLAR


BEAR


HYENA


NEBULAE


DOG


HAIR


RIVERS


GULL

TEETH


COMETS

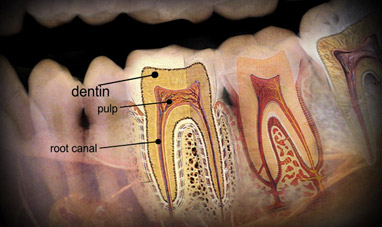
THE MOON

QUANTUM PHYSICS


COBRA

THE HEISENBERG PRINCIPLE


STARS


HERMIT CRAB


ELECTRIC CAR

THE LIVER


SHEEP


FROG


RAVEN


FLY


STORK


FACEBOOK


ARCHIMEDES' PRINCIPLE

FORCE, EQUILIBRIUM AND LEVERAGE


METEORITES


OIL